Vet's Best Friend: How to Buy a Veterinary Chemistry Analyzer
Vet chemists use chemical testing and analytical instruments to identify the types and concentrations of compounds in samples. These tests can be time-consuming, expensive, and often inaccurate. Vet chemists need reliable instruments to analyze their samples and get accurate results. Buying a veterinary chemistry analyzer is one of the first steps when buying new laboratory equipment. As there are many options available on the market, it’s important to understand what features different equipment comes with so you can make an informed decision. Here’s everything you should know before buying a vet chemistry analyzer
What is a Veterinary Chemistry Analyzer?
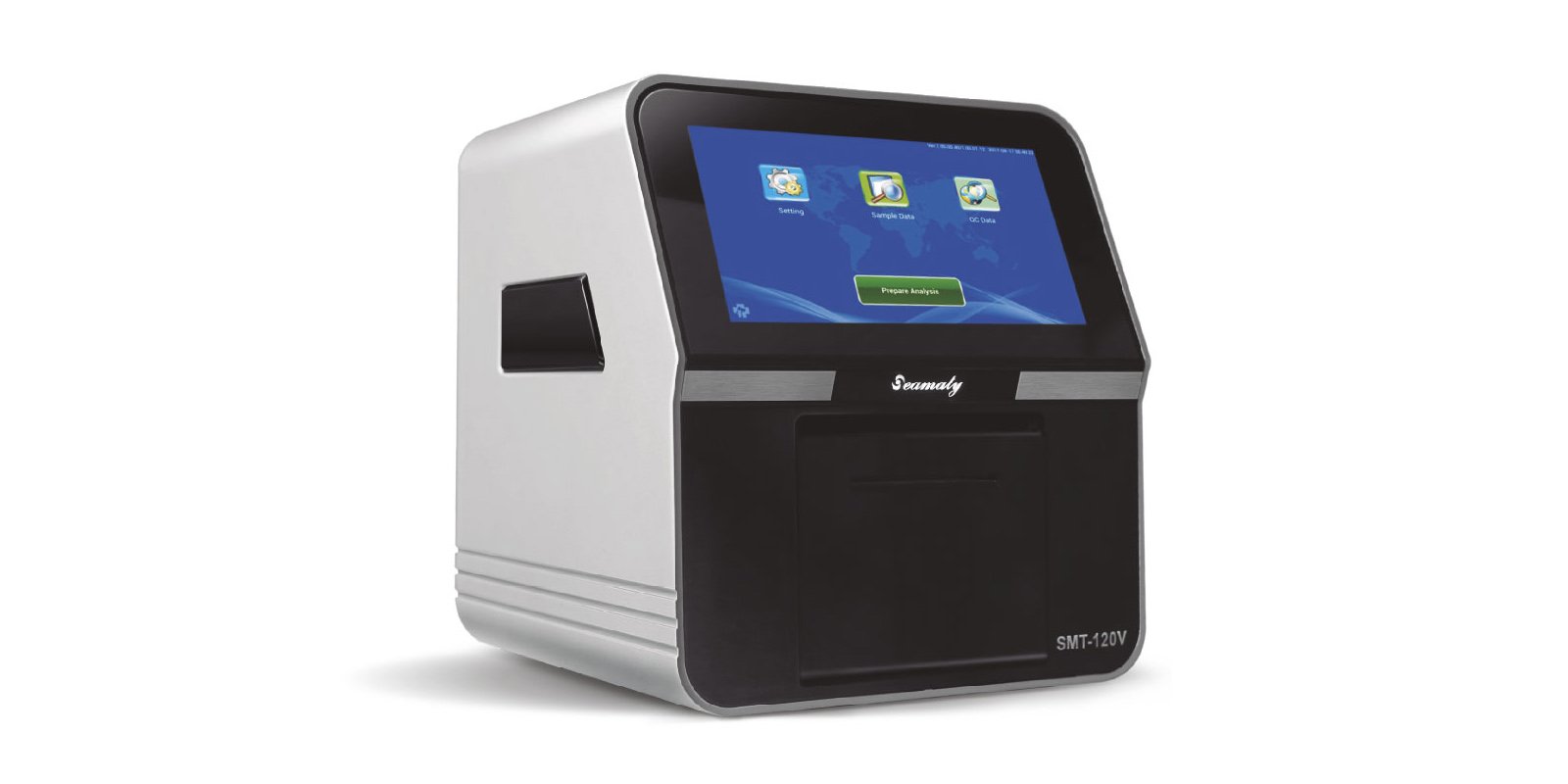
A veterinary chemistry analyzer detects and quantifies compounds in samples. The equipment may have a chromatograph, spectrophotometer, polarimeter, or other detection instrument. The vet analyzer performs a chemical analysis of blood, urine, or other sample material. These tests include blood glucose, electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, electrolytes, lipids (fats and lipids), blood hemoglobin, blood albumin, blood protein, potassium, sodium, chloride, and other vital compounds that help diagnose diseases, detect food allergies and contamination, and monitor medications in pets. Vet chemistry analyzers can also quantitate compounds. This means they can measure the amount of a particular compound present in a sample. Quantitation is helpful in some cases, such as when a patient’s condition is very bad and the doctor wants to know if the dosage is effective.
Types of Veterinary Chemistry Analyzers
Lab analyzers - These are the core of every veterinary lab. The majority of veterinary tests require lab equipment to be done correctly. These are the instruments that measure the physical properties of samples and generate results. An example of a lab analyzer is a mass spectrometer (MS) which is used to analyze compounds and identify them based on their atomic composition. GC/MS - This type of analyzer uses gas chromatography (GC) and mass spectrometry (MS) to separate compounds based on their molecular weight and identify them based on their atomic composition. GC is a method to separate compounds based on their boiling points, hence the name. The downside to GC is that it requires a hood. HPLC - The high-performance liquid chromatography method is the preferred method to analyze samples. This method separates compounds through liquid-phase chromatography, unlike GC which uses gas-phase chromatography. The HPLC method is easy to use and can be automated.
Vet Chemistry Analyzer Features to Consider
- Detection - The detection portion of the chemistry analyzer determines what compounds and concentrations are present in the sample. A GC/MS is the most accurate way to detect compounds. The other methods fall short in terms of accuracy.
- Accuracy - The accuracy of a veterinary chemistry analyzer refers to the level of accuracy in measuring what is actually present in the sample. Some labs use a method called relative accuracy, which means they estimate the amount of the compound expected.
Conclusion
Vet chemistry analyzers are used to detect and quantify compounds in samples. They operate similarly to clinical chemistry analyzers, except they are specifically for analyzing samples from animals. These analyzers come with different detection methods, accuracy, and can automate different functions such as injecting samples into a sample loop and cooling the temperature of the loop. Choosing the right veterinary chemistry analyzer is crucial for accurate and efficient testing.